Purpose:
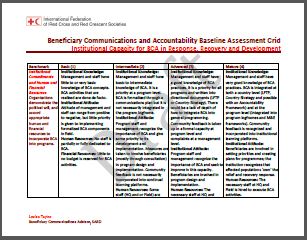
This document serves as a tool for assessing Beneficiary Communications and Accountability (BCA) in institutions.
Overview
The tool assesses:
- Institutional knowledge, capacity and commitment: institutional and human and financial resources; level of information sharing with communities; and participation and community engagement (beneficiaries have an opportunity to influence programme decisions and provide feedback).
- Emergency preparedness and response: preparedness activities; and response activities.
- Priority areas for beneficiary communication support: interventions; and tools.
- Country overview: demographics; health; disaster profile.
- Media landscape: SMS, internet, radio, TV, word of mouth, newspapers, media partnerships.
Usage: Guidance for project implementation; monitoring and evaluation
Audiences: Technical staff
Reference: International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (n.d.). Beneficiary Communications and Accountability (BCA) Baseline Assessment Grid. Institutional Capacity for BCA in Response, Recovery and Development. International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (pp. 1-10).
![]()