Purpose:
The aim of this manual is to give practitioners a tool to help them when designing an effective behavior change campaign. The methodology is explained step by step, all necessary skills and other requirements are described, and possible pitfalls are noted.
Overview:
The Risks, Attitudes, Norms, Abilities, and Self-regulation (RANAS) approach to systematic behavior change is an established method for designing and evaluating behavior change strategies that target and change the factors influencing a specific behavior in a specific population. In brief, it is an easily applied method for measuring behavioral factors, assessing their influence on behavior, designing tailored strategies that change behavior, and measuring the effectiveness of these. Although it was originally developed to change behavior in the water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH) sector in developing countries, it is applicable to a range of behaviors in various settings and populations.
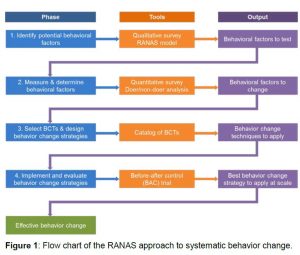
The RANAS approach to systematic behavior change involves four phases:
- Phase 1: Identify potential behavioral factors
- Phase 2: Measure the behavioral factors and determine those steering the behavior
- Phase 3: Select the behavior change techniques and develop appropriate behavior change strategies
- Phase 4: Implement and evaluate the behavior change strategies
Usage: Guidance for implementation
Audience: National Society WASH staff
See also:
- Methodological Fact Sheets – RANAS (Risks, Attitudes, Norms, Abilities and Self Regulation) approach to systematic behavior change
- For more information, refer to this external link.
Citation: Mosler, H.-J., & Contzen, N. (2016). Systematic behavior change in water, sanitation and hygiene. A practical guide using the RANAS approach. Version 1.1. Dübendorf, Switzerland: Eawag.
![]()